How does a top-loading washing machine work?
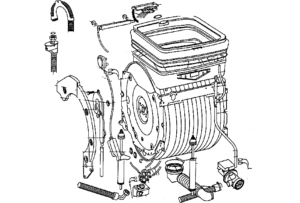 The desire to know the structure of a top-loading washing machine arises when there is a problem or malfunction. By understanding the components and sensors, you can check the machine yourself and fix the problem, saving a tidy sum. The task is generally not difficult - most “verticals” are similar in design and control. The main thing is to find time and act consistently.
The desire to know the structure of a top-loading washing machine arises when there is a problem or malfunction. By understanding the components and sensors, you can check the machine yourself and fix the problem, saving a tidy sum. The task is generally not difficult - most “verticals” are similar in design and control. The main thing is to find time and act consistently.
Components of the “vertical”
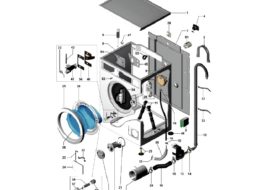
To get acquainted with the washing machine, you need to know all its components. Only by studying the names and purposes of the main components can one grasp the relationship of structural elements and their location. So, each “vertical” necessarily has the following details:
- electric motor;
- washing tank;
- metal drum with doors;
- drainage pump;
- rubber pipes and hoses;
- drum pulley;
- drive belt (if the washer does not have direct drive);
- powder and gel tray (also called powder receiver and dispenser);
- shock absorption system (springs, vibration absorbers);
On vertical washing machines, things are loaded through the top lid!
- tubular electric heater (TEH);
- drain filter;
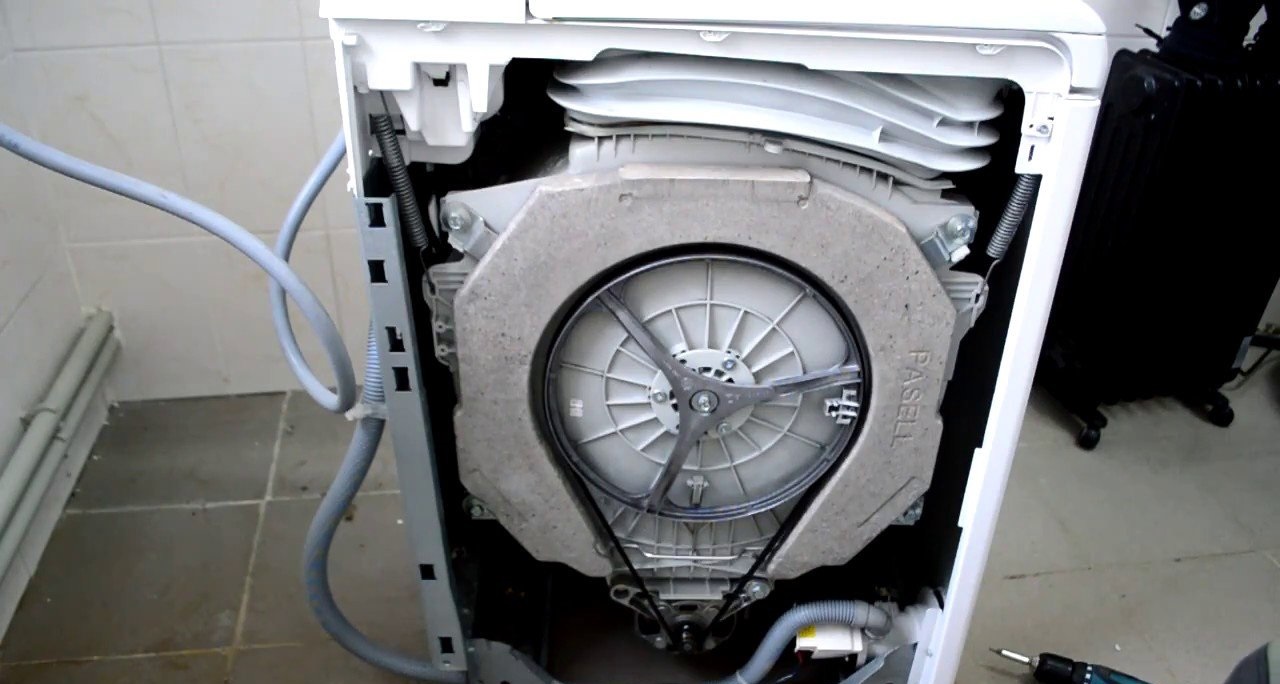

- control board (control module);
- dashboard;
- snail;
- thermistor;
- counterweights;
- electronic lock (UBL);
- inlet valve;
- cuff;
- pressure switch (water level sensor).
All components of the washing machine are “hidden” in a metal case. There is a “tidy” and a hatch cover on top, and blank panels on the sides. A tray is often attached to the bottom of the machine.
To check the machine and troubleshoot the problem, names alone are not enough - you need to know the device, the operating principle and the location of the parts. Let's look at the components in more detail.
Machine control center
Most modern washing machines have electronic controls. Unlike the “old” mechanics, everything here is performed and regulated by a module - a connecting unit consisting of sensors, conductors, tracks and microcircuits. The system works as follows:
- the user sets the cycle settings by pressing buttons or rotating the programmer on the dashboard;
- the control board records the selected parameters and issues a command to execute the program;
- the necessary system nodes are turned on;
- the wash starts.
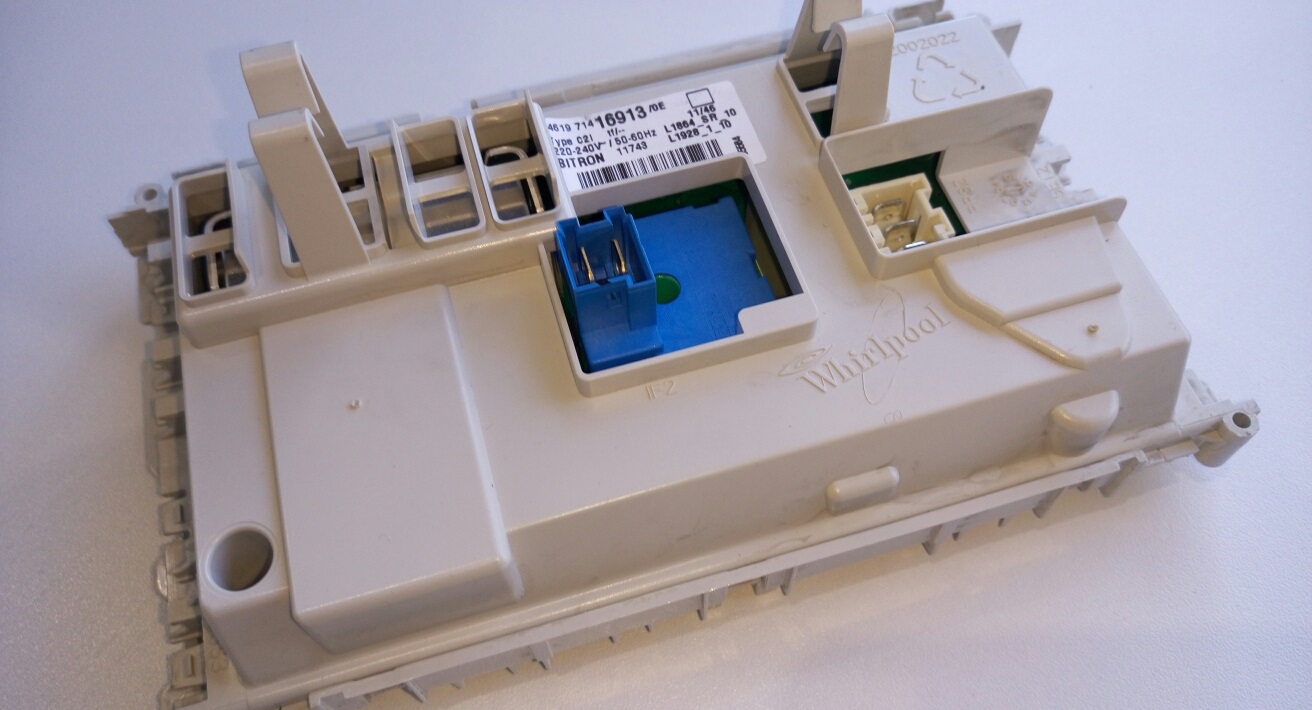

It is the control module that starts the washing machine: it processes information from the dashboard and transmits commands “through the chain” to the destination. Turning on the equipment, drawing water, accelerating the engine, draining - all this is performed only after “permission” from the electronic unit using a variety of triacs, sensors and contacts. Afterwards, the board controls the progress of work, monitoring the signals and data coming from the nodes. In the event of a failure or deviation, the device detects the problem and urgently shuts down the cycle.
It is not recommended to test and solder the board at home - it should be checked and flashed by specialists!
If there is a failure in the electronics system, the machine stops working: it does not turn on, does not respond to user commands, or freezes. It is difficult to find the problem, since either a separate track or the entire control unit as a whole could fail. In any case, the board loses control over the washing machine and, for security reasons, does not allow startup.
An electronic module is an extremely complex part. It is quite difficult to figure out on your own how it works and functions, especially for people far from electrical engineering. It’s better not to take risks and if you suspect a board malfunction, immediately contact a service center.
Parts responsible for clean water
The filling system in a vertical washer is represented by a pressure switch, hoses and an inlet valve. Water intake begins immediately after the user starts the program by pressing the “Start” button on the dashboard. The drum is filled according to the following scheme:
- the board receives a signal about the need for filling;
- pressure switch – water level sensor, measures the pressure in the tank and signals the level of filling;
- the module makes sure that there is no water in the tank and sends a dialing command to the valve;
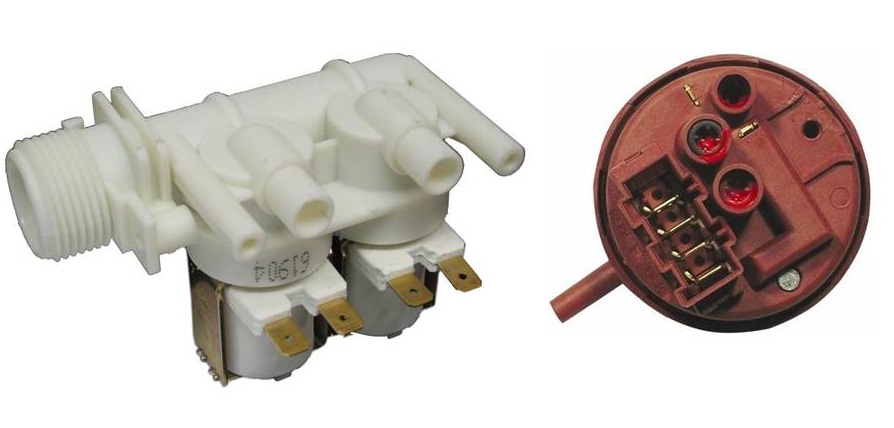

- voltage is applied to the intake valve, its membrane is activated, the flap rises;
- water from the water pipe flows into the machine through the inlet hose;
The pressure switch has a long tube that goes down into the tank and measures the pressure in it.
- the pressure switch controls the volume of water;
- when the required volume is reached, the pressure switch signals the unit;
- the module cuts off the current supply;
- the valve membrane closes;
- recruitment stops.
All elements of the filling system constantly interact, and the main “controller” is the water level sensor. Thanks to it, the tank is filled to a certain level, which prevents underfilling or overfilling.
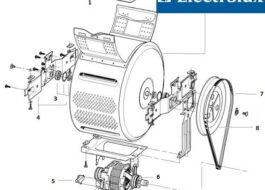
"Heart" of the machine
The “heart” of a washing machine is its engine. It is the electric motor that accelerates the drum shaft, ensuring the rotation of the cylinder at the desired speed. The number of revolutions is controlled by a tachogenerator, which clings to the engine and constantly monitors the pace, eliminating chaotic rotation and sudden changes in direction.
The driving force is an electric motor. Modern vertical machines are equipped with inverter motors, which are connected to the drum shaft directly, without the use of a drive belt. This system eliminates “middlemen”, which makes unwinding the cylinder more efficient, reliable and safe.
Some top-loading washing machines have commutator motors. Here the impulse from the motor is transmitted to the drum through a drive belt wrapped around the pulleys. This option is cheaper, but more unreliable: the elastic often falls off, breaking or stretching. The second disadvantage is the electric brushes, which during operation of the machine wear off on the engine body and periodically need to be replaced.
Where does the hot water come from?
As with front-mounted automatic machines, on vertical units a tubular electric heater – heating element – is responsible for heating. Once the user selects a mode and adjusts the temperature, the electronic board accepts the parameters and starts the heater. The part receives the signal, and upon completion of filling, its “spiral”, brought into the tank, begins to heat up.
To avoid overheating of the heating element, do not run three high-temperature cycles in a row!
The degree of heating is monitored by a thermistor - a temperature sensor. It looks like a metal tube and is located in the heating element itself. When the set degrees are reached, the device signals the module, which turns off the heater.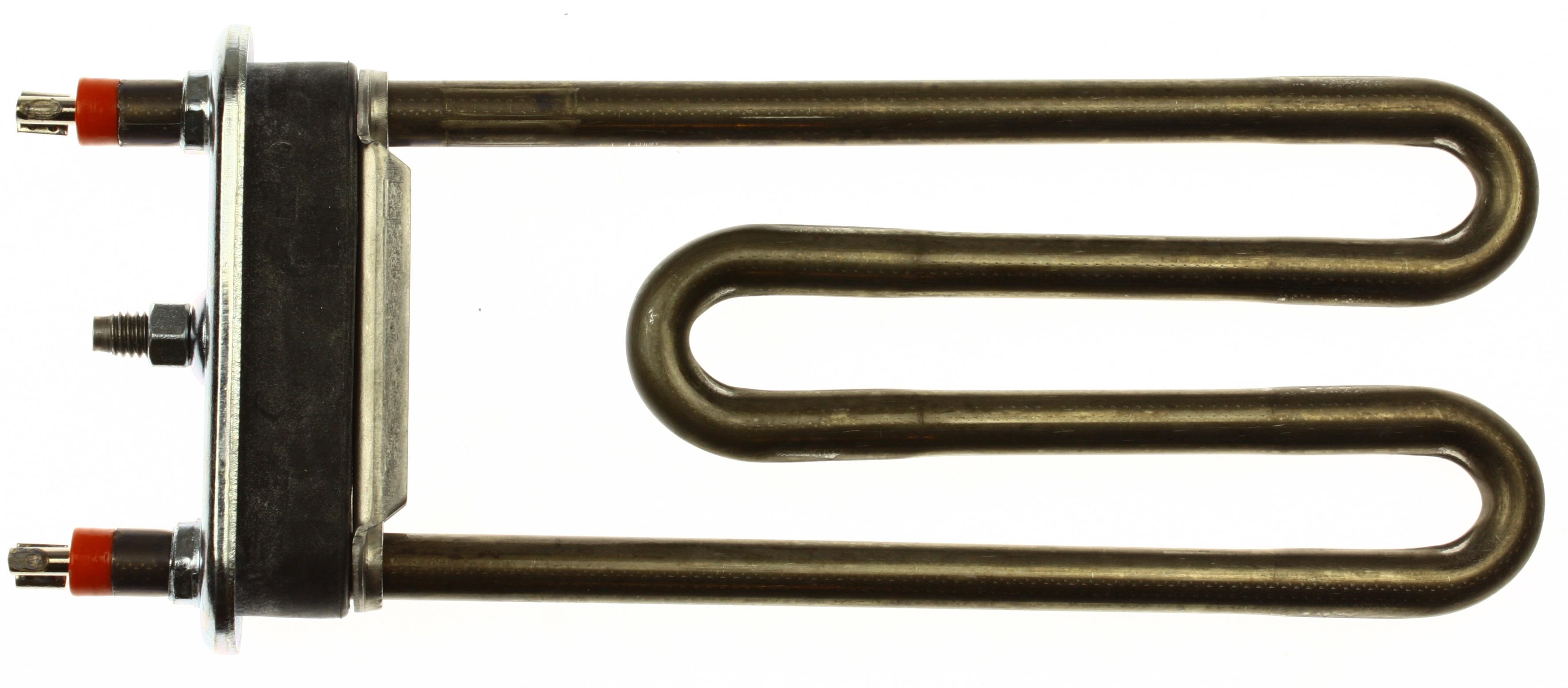
Weights and shock-absorbing system
When the drum unwinds, centrifugal force inevitably appears, which is absorbed by shock absorbers.They compensate for outgoing vibration, preventing the equipment from “jumping” around the room and hitting the wall. The stability of the washing machine is ensured by the following details:
- dampers - vibration dampers with a built-in spring, connecting the washing tank to the machine body;
- springs - the tank is suspended from the top and sides;
- counterweights are concrete blocks that are attached to the bottom or sides of the vertical, weighing down the entire structure.
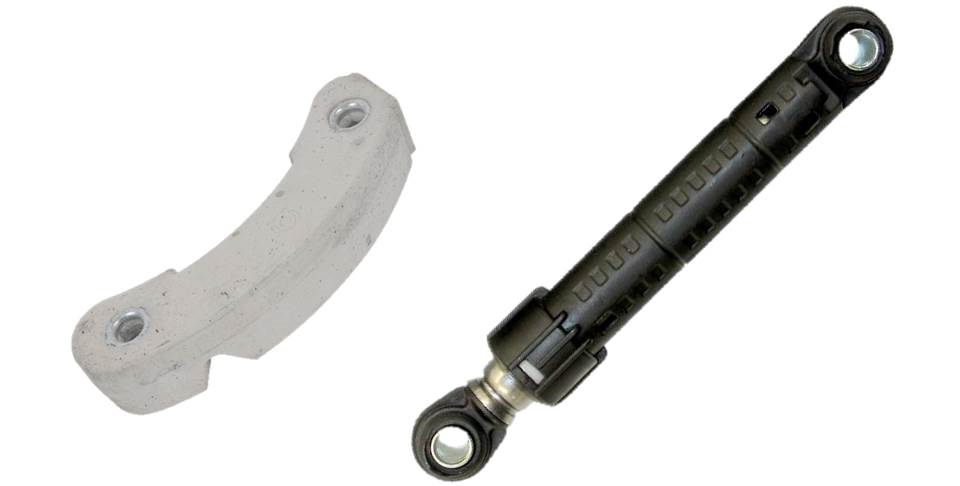

The shock absorption system takes on the entire “shock”. Due to constant vibration, dampers wear out, springs stretch, and counterweights become loose. Especially if the washing machine is not installed correctly or has been used for too long. In this case, it is necessary to tighten the fixing bolts and replace worn components.
Lock and seal
Each vertical is equipped with both mechanical and electronic. The mechanics are activated when the door is closed normally, when the locking “tongue” falls into the corresponding groove. The electronics turn on automatically when the washing program starts due to the UBL - blocking device. Thanks to the latter, the user will not be able to open the drum after the cycle has started.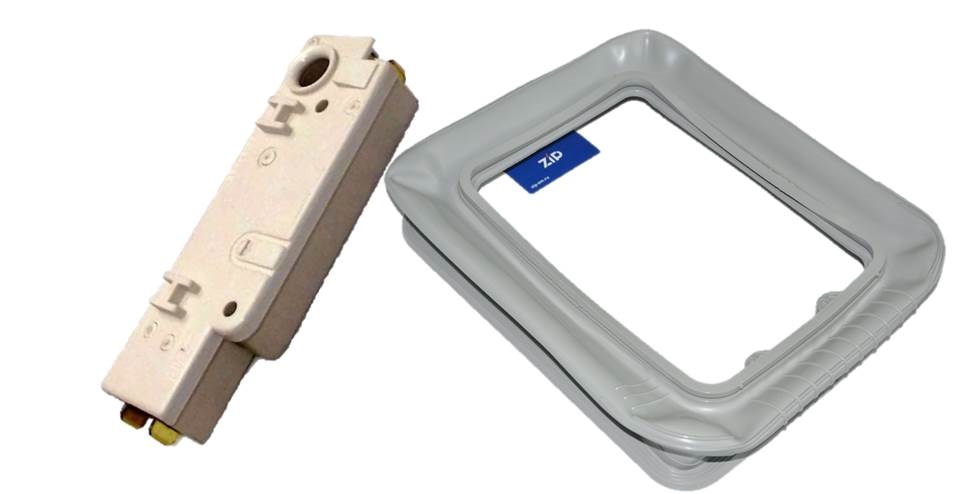
The seal of the hatch is also responsible for the tightness of the drum - a rubber seal stretched over the edges of the cylinder. It closes the gap between the tank and the body, preventing leaks and clogging of the structure. If the rubber band is damaged, do not start the wash, as water will begin to leak out.
Electric pump
A mandatory stage of any program is draining. To empty the tank, the machine is equipped with pipes, hoses, a pump and a drain filter. The key element of the drainage system is the pump, which pumps waste liquid from the drum into the sewer.
Vertical pumps are equipped with two types of pumps:
- synchronous;
- asynchronous.
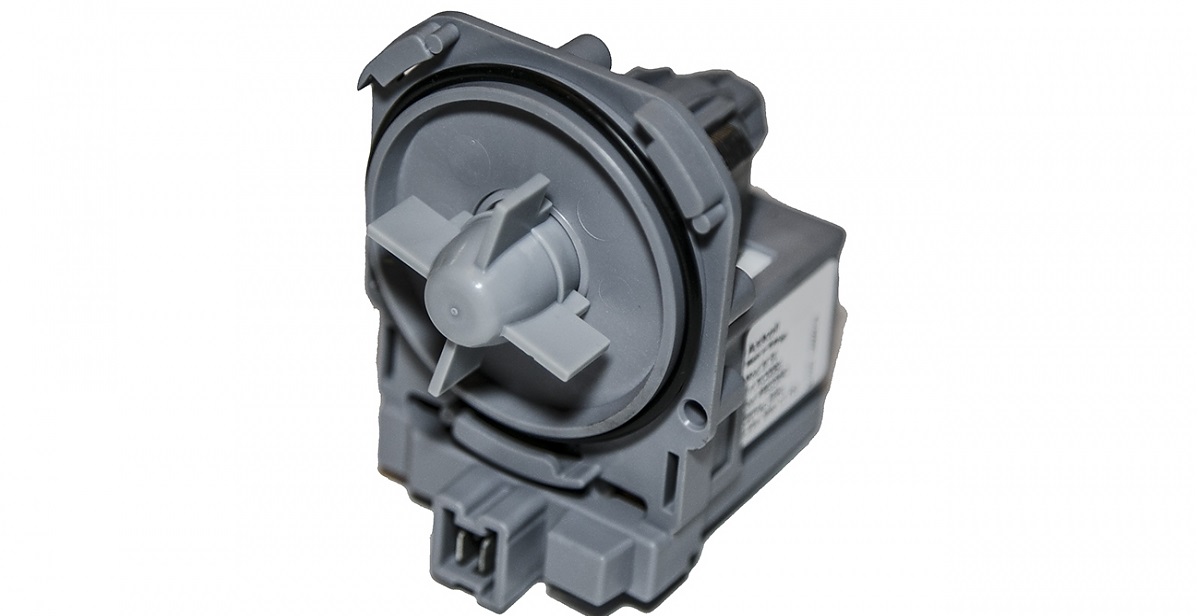

Each pump is designed the same. The device is started by a motor, which accelerates and spins the impeller - a screw that gives the water the desired trajectory. The pump is fixed to the cochlea, and a drainage hose and pipes are connected to it to drain the fluid.
The garbage filter protects the washing machine from clogging - most of the debris and dirt settle on its spiral!
Problems with pumping water rarely occur, and are not the fault of the pumps. The main reason for difficult drainage is that the hoses are clogged with debris that has gotten into the washer. The drainage filter suffers the most, where dirt settles and foreign objects get stuck. For prevention, you need to check the pockets and periodically clean the nozzle and all elements of the drain system.
Main tanks
The key element of the washing machine is the tank - a sealed plastic reservoir. It is tap water that is mixed with the powder. On vertical machines, the tank is positioned with the hole facing up, and on front ones – forward.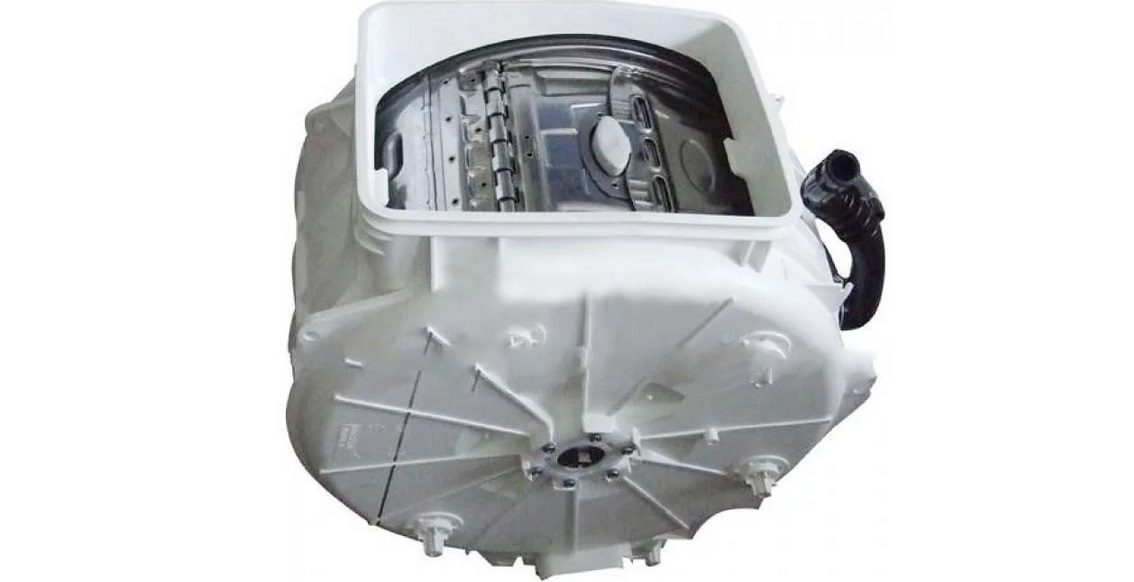
The drum is made of stainless steel. Clothes are placed in the cylinder, then the motor spins it to a predetermined speed. It is smaller, has perforated walls and rib punches - plastic blades that “mix” things and foam the powder.
The drum volume varies from 3.5 to 15 kg and depends on the capacity of the machine.
Hoses and powder box
A mandatory element of the washing machine is a powder receptacle. This is the plastic tray needed to add detergent. Powder or gel is taken from the bins in doses - at specified intervals and at certain stages of the program. The main thing is to fill the concentrate correctly, choosing the appropriate dispenser compartment.
Each powder receptacle has 3-4 compartments - for the main and pre-wash, bleach and conditioner.
We must not forget about the system of pipes through which water flows from the water supply into the drum, and then goes into the sewer. They “connect” the nodes of the machine, resembling human blood vessels. Separately, we note the hoses: inlet and drain. According to the first, water is poured into the equipment, and according to the latter, it is pumped out of the tank.
Automatic washing machines are multifunctional equipment that includes dozens of components, sensors and pipes. But if you want to understand the structure and mechanics, you can do it without any special preparation.
Interesting:
Reader comments
- Share your opinion - leave a comment


















Add a comment