Repair of the electronic module of the LG washing machine
 Repairing the control module of a washing machine requires certain skills and knowledge. If you have never seen a microcircuit or held a soldering iron in your hand, then it is better to entrust this work to a specialist. If you have at least some experience, you can try to cope with the task yourself.
Repairing the control module of a washing machine requires certain skills and knowledge. If you have never seen a microcircuit or held a soldering iron in your hand, then it is better to entrust this work to a specialist. If you have at least some experience, you can try to cope with the task yourself.
Repair of the electronic module of an LG washing machine is carried out in two stages. First you need to remove the board and find the burnt element. The second step will be to replace the semiconductor. Let's look into the nuances.
Which part does what?
When you first look at the LG SMA control module, you may be surprised at how many semiconductor elements it contains. If you check everyone, it will take a lot of time, so you need to understand which sensors are responsible for what. Then it will be possible to correlate this information with the “symptoms” of the breakdown and quickly detect the defect.
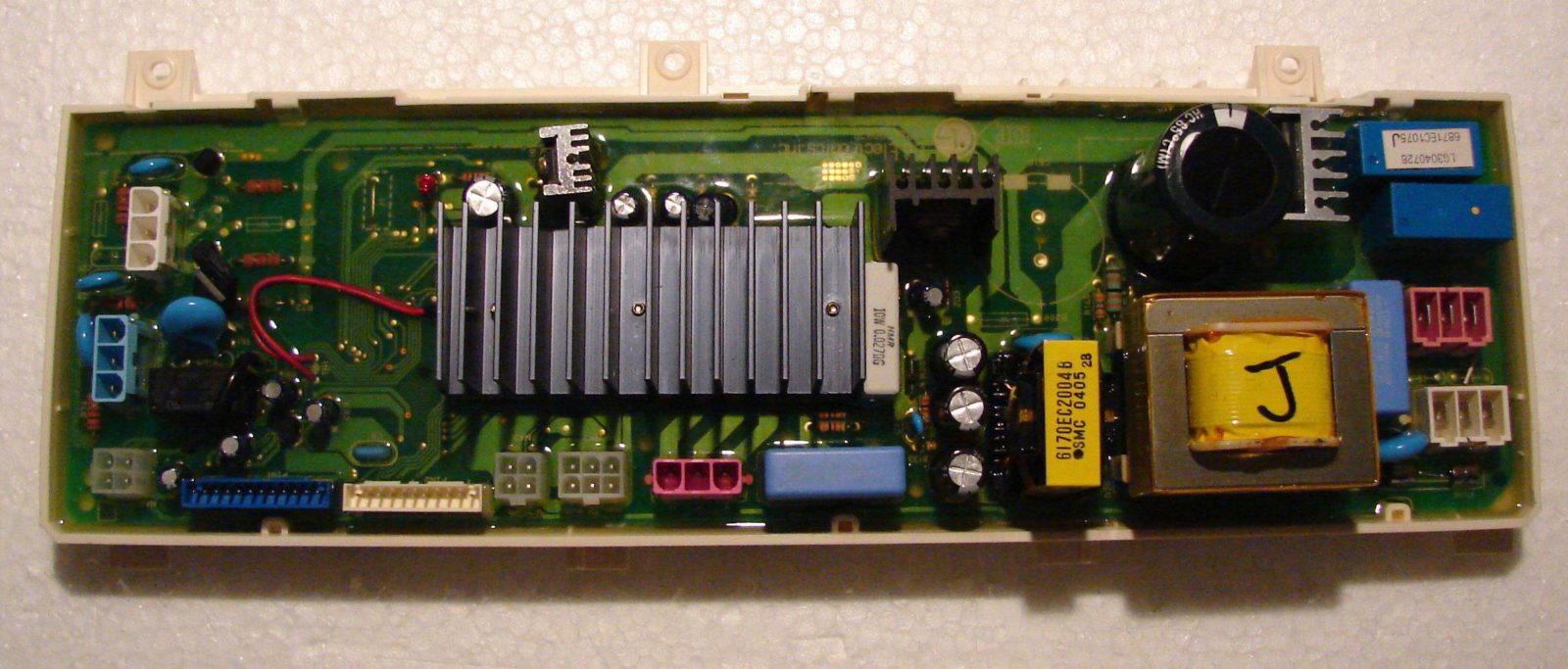
In general, the LG automatic machine module consists of two parts. This is the control panel and power unit. To get to the board itself, the part will have to be disassembled. Under the casing and compound there are semiconductor elements that control the operation of various components of the SMA.
Each semiconductor element is responsible for the operation of certain components of the LG washing machine.
Therefore, in order not to check every semiconductor, think about what exactly you didn’t like about the machine’s operation. If it simply stops turning on, you will have to test the sensors responsible for powering the device. If problems have been noted with the inverter motor, pay close attention to the HS1 power assembly, which is used to control the drive motor. Let's deal with everything in order.
On the left side of the control module there are elements responsible for powering the machine. This:
- integrated stabilizer KIA7805, designated U14 on the board;
- pulse converter based on PWM controller STR-A6059M;
- mains rectifier and filter (designated BD1 and CE4);
- protective varistor (Z2);
- mains fuse;
- key converter chip (designated U12);
- pulse transformer SMPS;
- diode D13, capacitor CE2;
- diode D11, capacitor CE8, power channel 9V;
- diode D12, capacitor CE9, power channel 12V;
- diode D14, capacitor CE6, power channel 12V;
- diode D6, zener diode ZD1, transistor Q1, resistor R103;
- resistor R74, also known as 205;
- optocoupler U15, transistor assembly U3;
- U13 processor;
- relay X1 (it is also connected in series to the heating element circuit);
- integrated voltage stabilizer 5V, designated U

The next element on the control board is the temperature sensor. This includes semiconductors:
- pin 4 (TH1) of connector RD6;
- resistor R12;
- 37 processor leg U
The following module semiconductors are responsible for the operation of the heating element:
- relay X1;
- 64 leg processor U13;
- 1 and 16 legs of assembly U3;
- relay X2;
- 24 leg processor U13;
- transistor Q7.
The module also has a backup relay control channel. Components are installed optionally. We are talking about the following semiconductors:
- 75 processor leg U13;
- resistor R83;
- transistor Q5;
- relay X4;
- second contact of connector BL
The following are responsible for the operation of the pressure switch:
- resistors R6, R7;
- 67 leg of U13 processor.
The next block of semiconductors is responsible for the operation of the pre-wash compartment valve. This:
- 29 processor leg U13;
- 4 and 13 legs of U3 assembly;
- resistor R25, R29;
- optocoupler U8;
- triac TR3;
- pin 1 of connector YL4.

The following are responsible for the operation of the main wash compartment valve:
- 31 U13 processor legs;
- 6 and 11 legs of assembly U3;
- resistor R23, R27;
- optocoupler U6;
- triac TR5;
- pin 4 of connector YL4.
The following circuit controls the hot water fill valve:
- 31 U13 processor legs;
- 6 and 11 legs of assembly U3;
- jumper J1;
- resistor R24, R28;
- optocoupler U7;
- triac TR4;
- second contact of connector YL4.
Semiconductors are responsible for the operation of the SMA drain pump:
- 61 U13 processor legs;
- resistor R77, R79, R82;
- transistor Q4, Q3;
- optocoupler U4;
- triac TR20;
- pin 4 of connector BL4.
If there are problems with the SMA hatch locking device, pay attention to the following block of elements:
- 27 processor leg U13;
- 2 and 15 legs of U3 assembly;
- resistor R21;
- optocoupler U2;
- relay X3;
- pin 1 of connector BL4.
The following are responsible for the operation of the Hall sensor, which controls the engine speed:
- pin 4 and 6 of connector BL6;
- resistor R44, R60;
- 3,4,5,6 legs of U1 chip;
- 19.20 processor leg U
If the washing machine motor stops working, test the following circuit:
- 17 processor leg U13 – power assembly HS1 (output stages and drivers) – microcircuit U1;
- comparator from the U11 microcircuit – storage choke RA – resistor R58, R57;
- 6.7 legs of comparator U11 – control of supply voltage 300V, the signal goes through a circuit with diode assembly BD1, resistor R70 and 41 legs of processor U
Resistors R73, R72 and 73, 74 legs of the U13 processor are responsible for the operation of the program switching selector.
As you can see, there are plenty of semiconductor elements on the board, so repairing the control module may be overwhelming for beginners who know nothing about microcircuits. If such concepts as resistors, relays, optocouplers do not surprise you, and you roughly understand how circuits are built, then you can try to repair the unit yourself.
Typical problems
Failures such as damage to the electronic module rarely occur with LG washing machines. Usually, it is not the control unit that is to blame, but some component or sensor. For example, if the machine does not turn on, you should not immediately disassemble the board - first check the socket, power cord, plug, noise filter, start button.
However, in rare cases, the problem will actually be in the control module. We'll tell you how to check the board in case of certain breakdowns of the CMA.
- The washing machine does not turn on, but the indicator on the electronic module is on. First of all, the turn-on signal circuit is checked to see whether it arrives after pressing the button on the 63rd leg of the U13 processor (via the optocoupler U15 and pins 13 and 14 of the U3 assembly). If everything is good, the 9V power channel is tested, see if the specified voltage goes to the relay winding X1.
- The machine turns on, but while the engine is running, the LE error appears on the display. Typically, such a malfunction is caused by damage to the Hall sensors and their circuits. You will need to check and replace the current-limiting SMD resistors on the module. You will first need to remove the compound on the tachometer block.
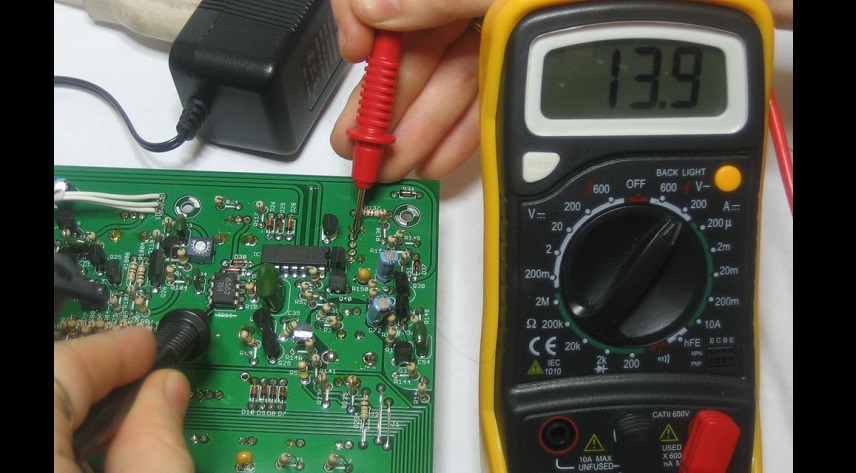
- The washer turns on, but the motor does not run. In this case, the PF error appears on the display. Typically, such a breakdown is associated with a lack of 300 V power supply on the HS power assembly. First, the integrity of the FUSE1 fuse is checked, and then the semiconductors of the BD1 circuit - HS1 assembly - resistor R70 for 41 legs of the U13 processor.
- If, after turning on the CMA, a CE error appears, it means that there is an overcurrent in one of the output stages of the assembly or a defect has appeared in the control circuit (resistor R58, R57, pins 6 and 7 of the comparator U11 on the 17th leg of the processor U13). Then you will need to replace the HS assembly. It is also worth checking the integrity of the motor windings; perhaps it is a matter of interturn short circuits.
- The machine turns on, but the cycle does not start due to error de. This means the hatch door is not locked. The serviceability of optocoupler U2 and all elements of its circuit (connector BL4, resistor R21, 27 legs of processor U13) is checked.
- If the washing machine refuses to drain water, and all possible blockages of hoses, sewers and pump breakdown are excluded, a block of elements is tested: resistors R77, R79, R82, transistor Q4, Q3, optocoupler U4, triac TR
Before testing the control module, make sure that the problem is not due to failed SMA components. Only when failures of other parts have been ruled out, start diagnosing the control board. Not all semiconductors need to be checked, but only those that correspond to the “symptoms” of the malfunction.
Checking and replacing the faulty element
Checking and repairing the SMA control module is complicated by the fact that the board is filled with compound. In addition, the unit is often protected by a casing, which also needs to be removed. Algorithm of actions:
- run a slotted screwdriver along the inner perimeter of the casing to remove the sealant from the edges of the board;
- deepen the groove along the perimeter of the module in the gap between the board and the casing;
- insert a thin screwdriver between the casing and the control board into the corner where the network transformer is located. Carefully lift the unit and remove it from the housing. Be careful not to damage the chip;
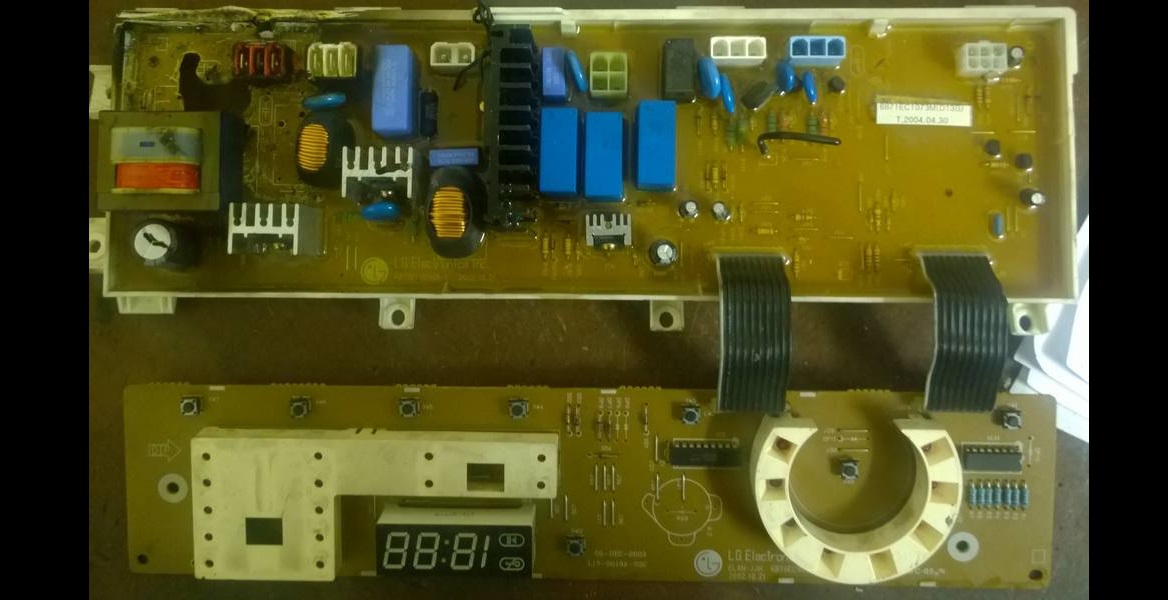
- after removing the board, remove any remaining sealant from it;
- repair the required section of the board (usually the damaged semiconductor element is soldered off and replaced with a similar one);
- coat the area with a protective varnish, for example, Plasik70 (for installation work).
Experienced repairmen do not remove the entire protective casing, but cut a hole in it that allows access to the damaged area.
For example, a specialist understands that the problem is in the semiconductors responsible for the operation of the drain pump. To avoid having to remove the entire casing, he cuts a hole in the lower right corner. This makes it possible to test the necessary elements.
It is necessary to work with the LG CMA electronic module with extreme caution. When removing the board from the casing, there is a high probability of damaging the microcircuits. Therefore, if you are not confident in your abilities, it is better to send the washing machine to a service center for repair.
Interesting:
Reader comments
- Share your opinion - leave a comment

















Add a comment